Antimicrobial Spectrum on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
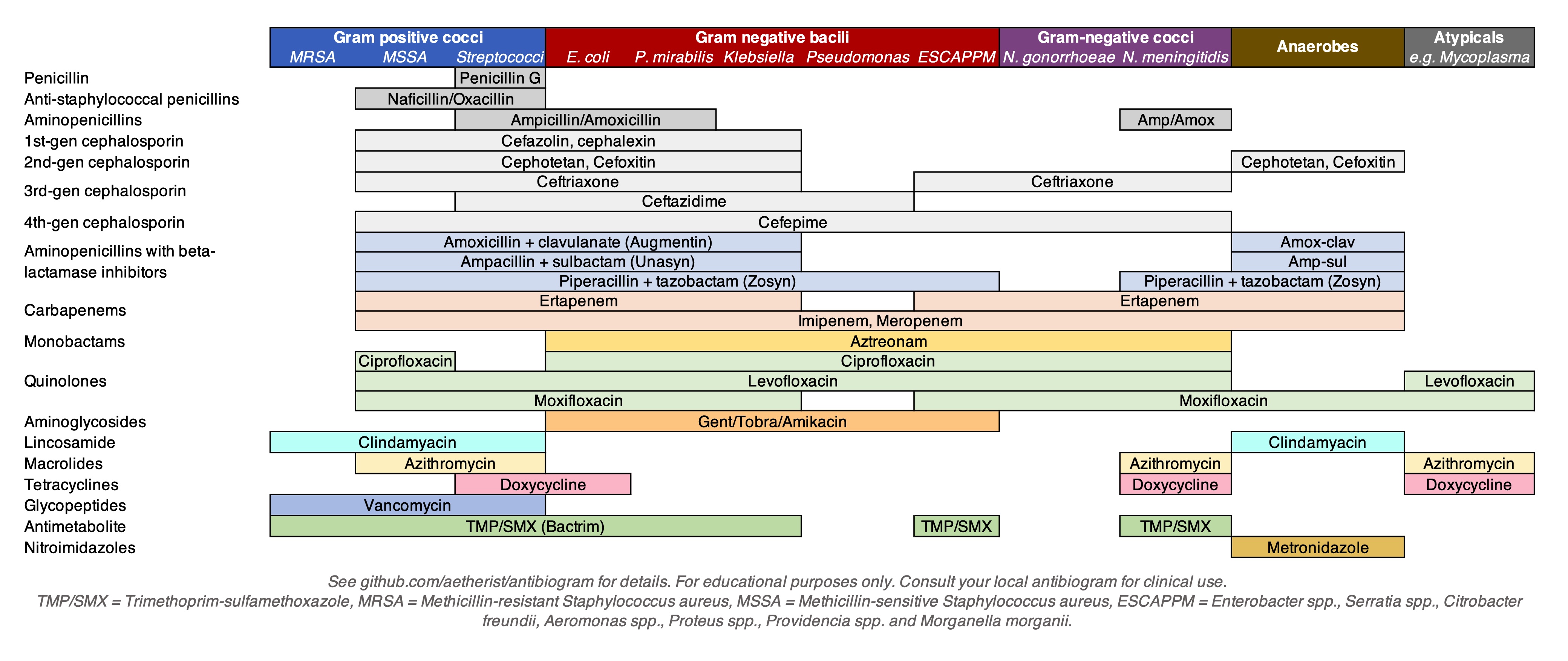 The antimicrobial spectrum of an antibiotic means the range of
The antimicrobial spectrum of an antibiotic means the range of
Healthcare Infection Control Practices Advisory Committee
(HICPAC) recommends the use of narrow-spectrum antibiotics whenever possible.
 The antimicrobial spectrum of an antibiotic means the range of
The antimicrobial spectrum of an antibiotic means the range of microorganism
A microorganism, or microbe,, ''mikros'', "small") and ''organism'' from the el, ὀργανισμός, ''organismós'', "organism"). It is usually written as a single word but is sometimes hyphenated (''micro-organism''), especially in olde ...
s it can kill or inhibit. Antibiotics can be divided into broad-spectrum antibiotic
A broad-spectrum antibiotic is an antibiotic that acts on the two major bacterial groups, Gram-positive and Gram-negative, or any antibiotic that acts against a wide range of disease-causing bacteria. These medications are used when a bacterial ...
s, extended-spectrum antibiotics and narrow-spectrum antibiotic
A narrow-spectrum antibiotic is an antibiotic that is only able to kill or inhibit limited species of bacteria. Examples of narrow-spectrum antibiotics include fidaxomicin and sarecycline.
Advantages
* Narrow-spectrum antibiotic allow to kill or ...
s based on their spectrum of activity. Detailedly, broad-spectrum antibiotics can kill or inhibit a wide range of microorganisms; extended-spectrum antibiotic can kill or inhibit Gram positive bacteria and some Gram negative bacteria; narrow-spectrum antibiotic can only kill or inhibit limited species of bacteria.
Currently no antibiotic's spectrum can completely cover all types of microorganisms.
Determination
The antimicrobial spectrum of an antibiotic can be determined by testing its antimicrobial activity against a wide range of microbes ''in vitro
''In vitro'' (meaning in glass, or ''in the glass'') studies are performed with microorganisms, cells, or biological molecules outside their normal biological context. Colloquially called " test-tube experiments", these studies in biology ...
''. Nonetheless, the range of microorganisms which an antibiotic can kill or inhibit ''in vivo'' may not always be the same as the antimicrobial spectrum based on data collected in vitro.
Significance
Narrow-spectrum antibiotics have low propensity to induce bacterial resistance and are less likely to disrupt themicrobiome
A microbiome () is the community of microorganisms that can usually be found living together in any given habitat. It was defined more precisely in 1988 by Whipps ''et al.'' as "a characteristic microbial community occupying a reasonably wel ...
(normal microflora
Microbiota are the range of microorganisms that may be commensal, symbiotic, or pathogenic found in and on all multicellular organisms, including plants. Microbiota include bacteria, archaea, protists, fungi, and viruses, and have been found to ...
). On the other hand, indiscriminate use of broad-spectrum antibiotics
A broad-spectrum antibiotic is an antibiotic that acts on the two major bacterial groups, Gram-positive and Gram-negative, or any antibiotic that acts against a wide range of disease-causing bacteria. These medications are used when a bacterial i ...
may not only induce the development of bacterial resistance and promote the emergence of multidrug-resistant organisms, but also cause off-target effects due to dysbiosis. They may also have side effects, such as diarrhea or rash. Generally, a broad antibiotic has more clinical indications, and therefore are more widely used. ThHealthcare Infection Control Practices Advisory Committee
(HICPAC) recommends the use of narrow-spectrum antibiotics whenever possible.
Examples
* Broad-spectrum antibiotic:Ciprofloxacin
Ciprofloxacin is a fluoroquinolone antibiotic used to treat a number of bacterial infections. This includes bone and joint infections, intra abdominal infections, certain types of infectious diarrhea, respiratory tract infections, skin inf ...
, Doxycycline, Minocycline
Minocycline, sold under the brand name Minocin among others, is a tetracycline antibiotic medication used to treat a number of bacterial infections such as pneumonia. It is generally less preferred than the tetracycline doxycycline. It is also ...
, Tetracycline
Tetracycline, sold under various brand names, is an oral antibiotic in the tetracyclines family of medications, used to treat a number of infections, including acne, cholera, brucellosis, plague, malaria, and syphilis.
Common side effects in ...
, Imipenem
Imipenem (trade name Primaxin among others) is an intravenous β-lactam antibiotic discovered by Merck scientists Burton Christensen, William Leanza, and Kenneth Wildonger in the mid-1970s. Carbapenems are highly resistant to the β-lactamase enz ...
, Azithromycine
*Extended-spectrum antibiotic: Ampicillin
Ampicillin is an antibiotic used to prevent and treat a number of bacterial infections, such as respiratory tract infections, urinary tract infections, meningitis, salmonellosis, and endocarditis. It may also be used to prevent group B stre ...
* Narrow-spectrum antibiotic: Sarecycline, Vancomycin
Vancomycin is a glycopeptide antibiotic medication used to treat a number of bacterial infections. It is recommended intravenously as a treatment for complicated skin infections, bloodstream infections, endocarditis, bone and joint infections, ...
, Isoniazid
Isoniazid, also known as isonicotinic acid hydrazide (INH), is an antibiotic used for the treatment of tuberculosis. For active tuberculosis it is often used together with rifampicin, pyrazinamide, and either streptomycin or ethambutol. For la ...
See also
* Antibiotic *Methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus
Methicillin-resistant ''Staphylococcus aureus'' (MRSA) is a group of Gram-positive bacteria that are genetically distinct from other strains of '' Staphylococcus aureus''. MRSA is responsible for several difficult-to-treat infections in human ...
(MRSA)
References
{{Medicine, state=collapsed Antibiotics Clinical pharmacology